-

Current policies adopted for Research, Technology and Innovations in high- and upper middle- income countries are resource intense and focused on global competitiveness; Courtesy: Pixabay

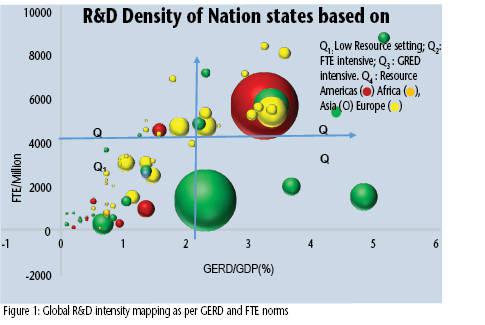
SDG-9 recognises that the manufacturing activities in the world serve only about 14 per cent of the global population through employment creation. In fuller realisation of SDG-9 targets, the possible roles of research, technology and innovation in job creation in developing economies are duly acknowledged. Current policies adopted for Research, Technology and Innovations in high- and upper middle- income countries are resource intense and focused on global competitiveness. Such a model could well bypass the inclusive development targets of SDG-9. A revisit of policy perspectives for supporting industrial infrastructure based on innovations for development in low resource setting with a ‘pro-poor agenda’ is in order. The inclusive developmental agenda of SDG-9 calls for attention to the purpose of innovations. An alternate model based on ‘collaborative’ in place of ‘competitive’ excellence seems relevant. An analysis of resource intense research model for innovations: Currently, the research intensity of a nation state is measured in terms of the number of Full Time Equivalents (FTE) of R&D professionals and Gross Expenditure on R&D (GERD) as a percentage of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). The investments in GERD of the USA were $612 billion in 2020. For serving a population of 7.5 billion, global annual GERD needs to be in the range of $13.5 trillion on Purchase Power Parity terms at the rate of the USA per FTE. R&D investments at such scales are unsustainable and could well fail to serve the needs of nations in low resource setting. Resource intense innovation models tend to adopt public:private investments in the ratio of 1:2-3. The pandemic showcased the aftermath of healthcare as business and R&D for the private good. The innovation sector in the world is driven by competitive excellence and first mover advantages for investors with speed as premium in the marketplace. Many nations had to invest public funds in R&D to combat Covid. SDG-9 reveals the essentiality of people-centric priorities for R&D. The current innovation policies lead to multiplication of investments for competitive advantage. Consequently, costs of innovations from research from countries in Quadrant (Q4) in Figure 1 become high. The technology sector is market-driven. It is focused on market share. The current research, technology, and innovation system from Q4 could, at best, serve 30-40 per cent of the global market on account of the affordability challenge of low- and lower middle-income countries. People in many Q1 countries are either under- or unserved. For the serving technology needs of low- and lower middle-income countries, an alternate model for technology development is necessary.
An alternate model: A country like India is known to invest about $65 billion per year with annual investments per FTE matching those of many OECD countries. Her investments of GERD are about 90 per cent of the combined value of 35 low- and 55 lower middle-income countries. The affordability challenge for infrastructure, innovation and industry of these nations is large. Indian innovation and industrial infrastructure are able to serve the pro-poor agenda of many nations in a low resource setting.
The ability of Indian vaccine manufacturing at the time of the pandemic for serving the needs of many nations has been showcased. The research innovation on a vaccine occurred in one country. Manufacturing based on that innovation was done in India. It is an excellent example of collaborative excellence as an alternate model.
Call for North-South-South collaboration: Technology and innovations developed through resource intense model in the North serve high- and upper middle-income economies. Several nations in the South are unable to create a resilient infrastructure, innovation ecosystem and industrial manufacturing capability based on resource-intense innovations.
A country like India in the South with credible research, technology and innovation infrastructure could well partner in a triangular collaboration playing a part in optimisation and contextualisation of innovations from the North. A triangular collaboration model for serving the needs of under- and un-served markets of the world could be a win-win formula and serve SDG-9 in a low resource setting. Collaborative excellence as an innovation in policy for delivering goodness as a value of SDG-9 is needed.
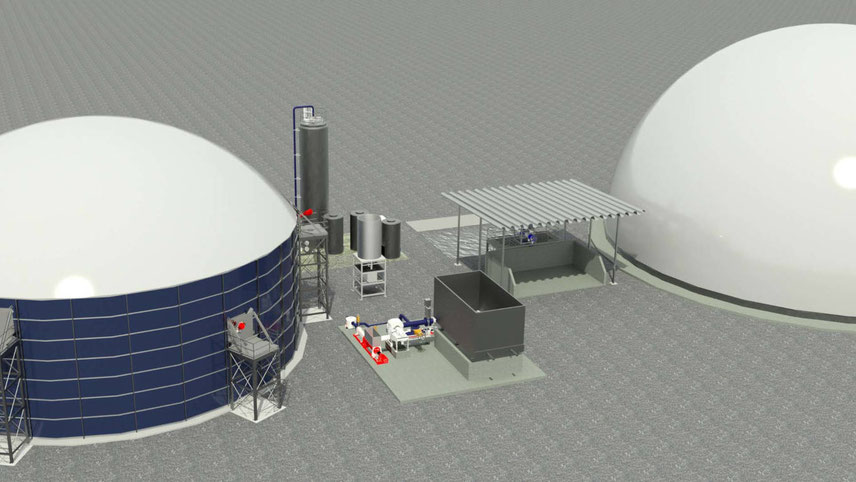
Biogas
BioEnergy will showcase its innovative biogas technology in India
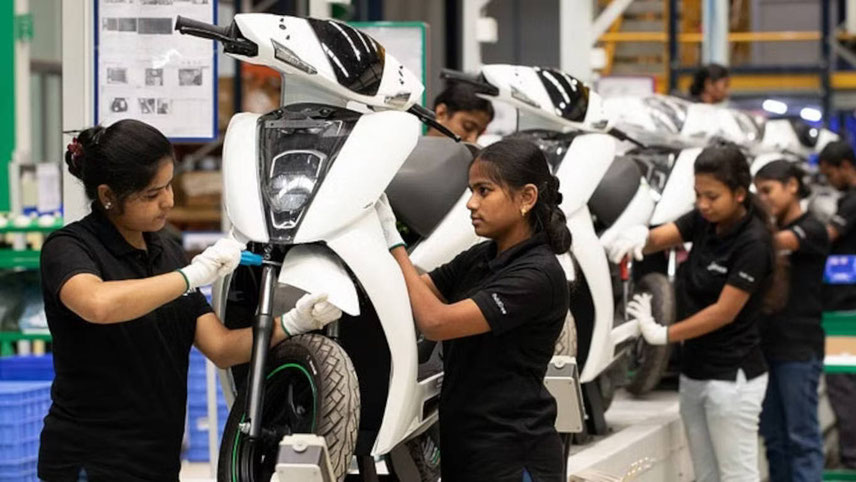
Mobility
Ather aims to produce 20,000 units every month, soon
Green Hydrogen
German Development Agency, GIZ is working on a roadmap for a green hydrogen cluster in Kochi
Renewable Energy
AGEL set to play a big role in India’s carbon neutrality target